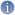Transportation and global warming
The Paris Climate Agreement emphasises the urgent need to accelerate climate action in order to achieve the global target to keep global temperatures well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, and pursue efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C. The Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) further recognises that in order to achieve this goal, the participation of both Parties and non-Parties, and voluntary contributions from stakeholders outside of the formal UNFCCC processes, will be needed.
To realise the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement, the world must go further and faster in delivering climate action before 2020. To achieve this, adequate flows of finance, technology, and capacity building must be enabled.
Exemple : Solutions to Global Warming in North America
Solutions to global warming in North America include reducing coal emissions, increasing the use of energy efficiency and renewable energy, greening transportation, and helping developing countries reduce deforestation.
The United States is often noted as the being the most significant contributor to historical emissions of global warming pollution. Most of these emissions occur when power plants burn coal or natural gas and when vehicles burn gasoline or diesel. There are concrete actions that citizens, businesses and policymakers can take to reduce global warming emissions. Experience has shown that government policies are critical to spurring and enabling global warming solutions and that individual actions alone will not solve the problem. While comprehensive climate and energy legislation has thus far failed to pass the United States Congress, there are a series of vital programs and strategies underway in the United States to reduce global warming emissions, such as:
|
Exemple : Climate Change and Transport in Asia
Asia and the Pacific's motorized transport emissions have become a significant contributor to the global problem of greenhouse gas emissions that lead to climate change. How can the region avoid a bleak future of congested roads, pollution, ill health, and economic damage?
Asia's cities suffer from high pollution levels, with as much as 80% attributable to transport.
Asian economies lose 2%-5% of their GDP every year due to road congestion.